Polymers Used in Plastic Moulding
First, we have to understand that what is Polymer. It is a class of molecules with large numbers of repeating structural units connected through covalent bonds. So how we know about different polymers? It is differed by repetition of many similar, identical or complementary subunits.
Polyethylene is the first choice for plastic moulding process and the reason is its availability, ease of use and also it has many suitable properties. There is 80-90 percent of polymers used in plastic moulding industry are polyethylene compounds (HDPE, LDPE and LLDPE). And also, PVC, nylons and polypropylene compounds are used.
Polyethene is widely used thermoplastic created through polymerization of ethylene.
It is also known as Polyethene, Polythene, PE, LDPE, HDPE, MDPE, LLDPE.
- LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene)
LDPE has a density range of 0.910 – 0.940 g/cm3. LDPE has a high degree of short and long chain branching means the chains do not pack into crystal structures. Due to this, it has less intermolecular forces and the instantaneous-dipole induced-dipole attraction is less. Which means it has lower tensile strength and increased ductility. The LDPE is created by free radical polymerization. LDPE gets its to flow properties from the high degree of branches with long chains.
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene)
HDPE has a density of equal or greater than 0.941 g/cm3. It has a low degree of branching gives stronger intermolecular forces and tensile strength. It can be made with chromium/silica catalyst, Ziegler-Natta catalyst or metallocene catalysts.
- MDPE (Medium Density Polyethylene)
MDPE has a density range of 0.926 – 0.940 g/cm3. The MDPE can be produced by chromium/silica catalysts, Ziegler-Natta catalysts or metallocene catalysts.
- LLDPE (Linear-Low Density Polyethylene)
LLDPE has a density range of 0.915 – 0.925 g/cm3. It is a substantially linear polymer and has significant numbers of short branches made by copolymerization of ethylene with a short chain of alpha-olefins like 1-butane, 1-hexene and 1-octene.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
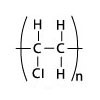
Polyvinyl Chloride Polymer
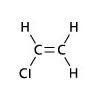
Vinyl Chloride Monomer (VCM)
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is widely used thermoplastic material for various application. To produced it, the required material is derived from Oil and Salt. The vinyl chloride monomer (VCM) is formed by mixing ethylene which is obtained from oil and Chlorine produced by electrolysis of salt water. The VCM molecules are polymerized to form PVC resin and along with different additives made customized PVC compound.
Nylons
Nylon is a group of plastics known as polyamides. It is used in the manufacturing of fiber and film and it is also used as a moulding compound.
There are many types of Nylon available like nylon 6, nylon 66, nylon 6/6-6, nylon 6/9, nylon 6/10, nylon 6/10, nylon 6/12, nylon 11, nylon 12. Nylon is used as homopolymer, copolymer or reinforced. Nylon mixes with other engineering plastics to create required material. It is suitable for injection molding, rotational moulding, casting or extrusion into film or fiber.
Chemical Composition
Polypropylene
The thermoplastic polymer, polypropylene also known as polypropene has properties between LDPE and HDPE and it is more versatile material available.
Chemical Composition
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is an opaque thermoplastic and amorphous polymer. It is a terpolymer consist of Acrylonitrile, Butadiene and Styrene. All these material mixes and creates a product which is flexible and light in weight and it is used in our many daily routine items.
The main benefit of using ABS that it improves impact resistance, toughness and heat resistance. If it is moulded on the high temperature it gives gloss and heat resistance to the product and if it is moulded on the low temperature it gives the highest impact resistance and strength to the product.
ABS is used in drain pipe systems, plastic clarinets, golf clubs heads, automotive parts, kitchen appliances and many more.
Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate plastics are naturally transparent amorphous thermoplastics. It is used in various products but most in where impact resistance and transparency are required like Bullet-Proof Glass. Opposite of different plastics Polycarbonate can goes to large plastic deformation without any crack or breaks.
It is widely used for greenhouses, DVDs, eyewear lenses, medical devices, automotive components and cellular phones.
High Impact Polystyrene
The high impact polystyrene (HIPS) is very popular and tough plastic in polystyrene family. Polystyrene itself is brittle but can be made more impact resistant if mix with other materials. It is made with modifying crystal styrene with rubber which gives it more impact resistance. HIPS is low cost, good dimensional stability and rigidity.
It is highly flammable but there are also flame retardant and high gloss grades are used for injection moulding.
